Advanced On Page Optimization Tactics I’m Going to Cover
If you are reading this, you should already be familiar with basic on page SEO principals involving H1, H2, H3 tags, content optimization, title tags, meta descriptions, etc. This tutorial will be covering more advanced topics such as Latent Semantic Indexing, Schema Markup, Preventing Duplicate Content with WordPress, Image File Compression, and more.
Ultimately, an SEO should be thinking about developing their content for a mobile audience, while keeping conversational search in mind. Google’s voice search isn’t striving to simply answer your questions, but they are trying to get Google to eventually have conversations with its users. This way, you can ask a question, Google will respond, where you can follow up with another question while Google continues to reply within the context of the conversation.
That said, before you can truly understand how to develop an on page strategy around these principles, you must first develop a deeper understanding of how Google makes conversational search possible.
Optimizing Your Content Using SEMrush Ideas & LSI
Latent Semantic Indexing is a method Google uses to index content. A typical search engine indexes content for a certain set of keywords by matching each keyword to words on a page.
Latent semantic indexing adds an important step to the document indexing process. In addition to recording which keywords a document contains, the method examines the document collection as a whole, to see which other documents contain some of those same words. Essentially, LSI looks for semantically related content rather than just keyword variations or densities on a page.
Fortunately, SEMrush has an awesome tool to help you optimize your content this way. Here’s how you set it up.
Step 1: Create a new project and set up position tracking before anything else
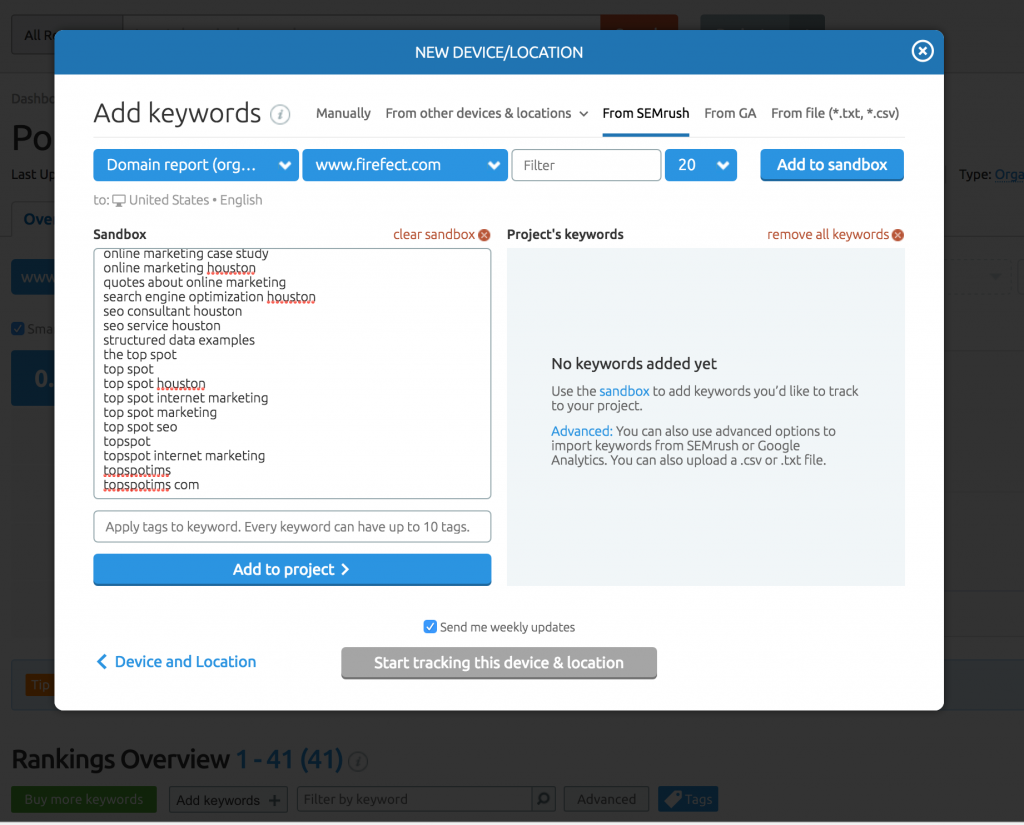
Choose how you want to source out your keywords. For the sake of this tutorial, I just allowed SEMrush to suggest a set of keywords for me based on the terms my competitors rank for.
Step 2: Start SEO Ideas
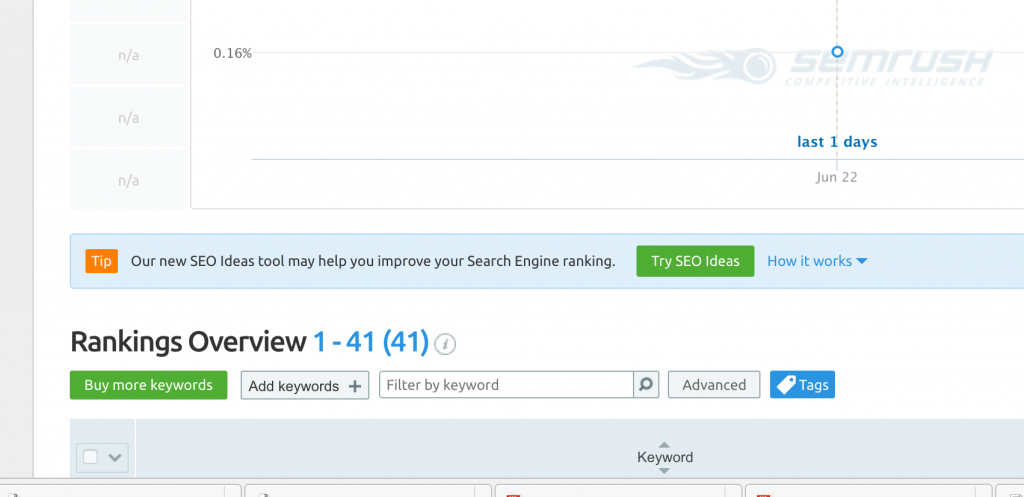
Once on the position tracking page, you’ll notice a small green button prompting you to Try SEO Ideas. Click that green button.
Step 3: Setup SEO Ideas
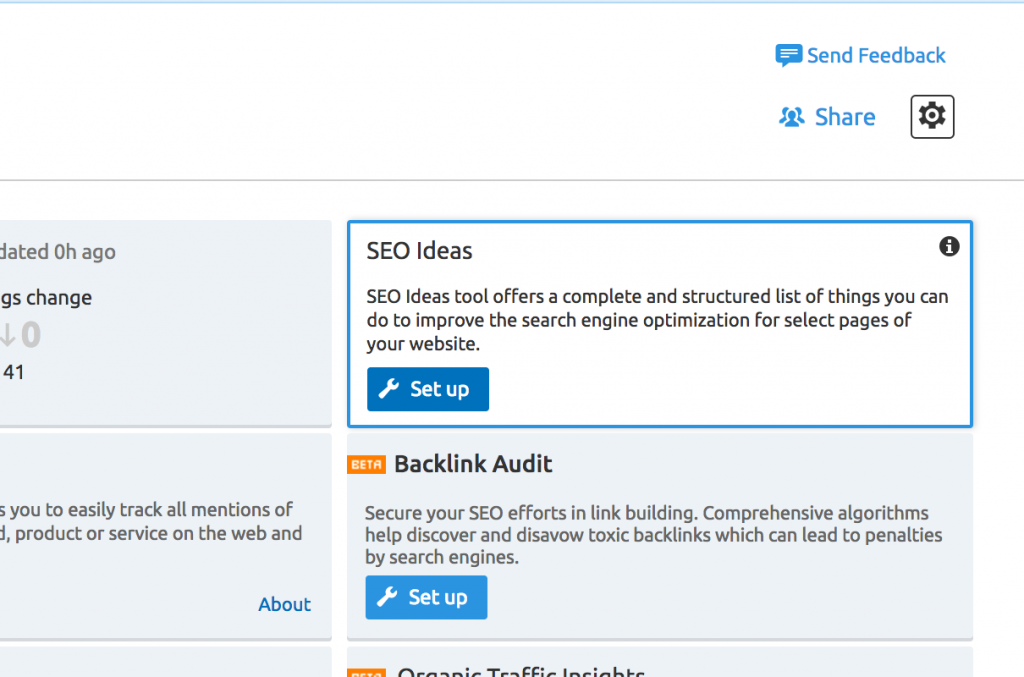
Step 4: Select your target location and run the SEO Ideas tool
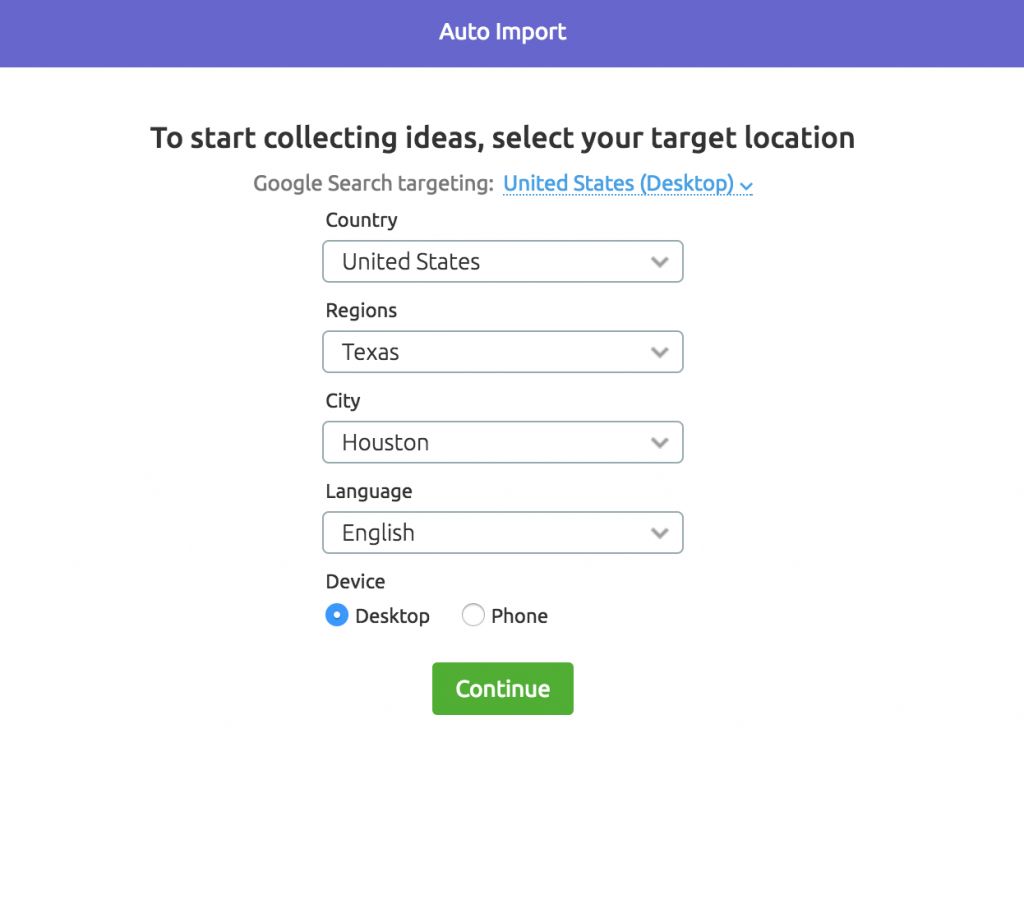
Allow SEMrush to Collect the Data
Once SEMrush has finished collecting all of the SEO Ideas data, jump in and take a look at the way the data has been segmented. It should categorize the data like so:
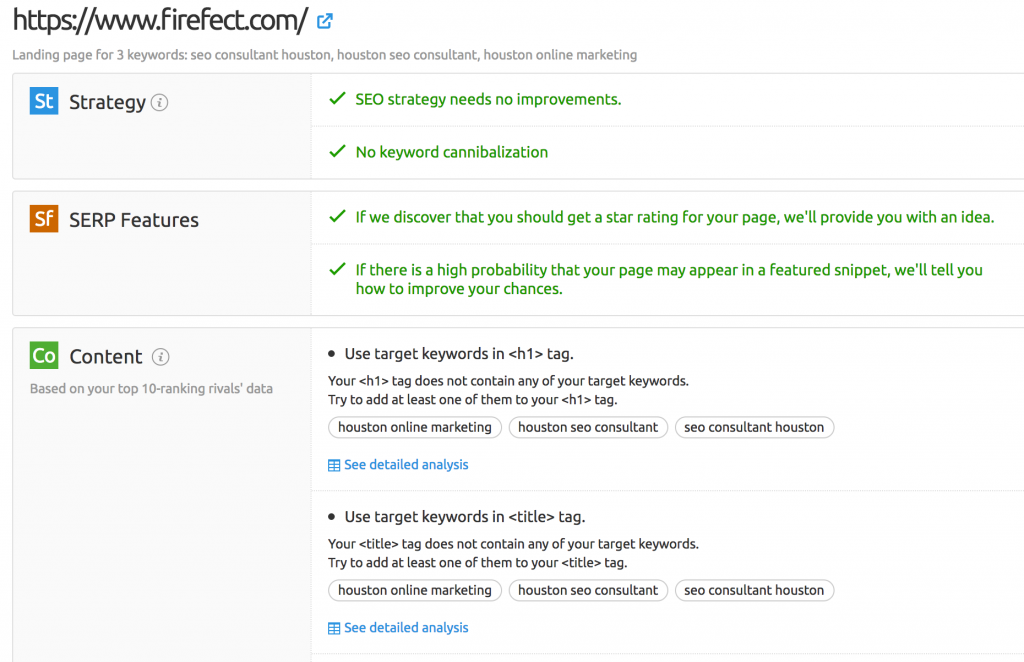
- Strategy
- SERP Features: Rich Snippets, Schema, etc.
- Content: Assesses prominent keyword usage based on your top 10-ranking rivals’ data, breaking the content down to each component of the web page’s structure (e.g. H1, H2, Title, Meta, body, anchor, etc.).
- Semantic: Suggests semantically relevant keywords to use based on your top 10-ranking rivals’ data.
- Backlinks: Automatically performs a backlink gap analysis to find common links your competitors have. This data is based on your top 10-ranking rivals’ data
- Technical Issues: To get ideas, you should first set up a site audit campaign on the Project Dashboard.
- User Experience: To get ideas, you should first Connect Google Account.
Start With SEO, Content Optimization Suggestions
Start off by clicking the See Detailed Analysis under any of the content recommendations. They will all take you to the same page; it will look like this:
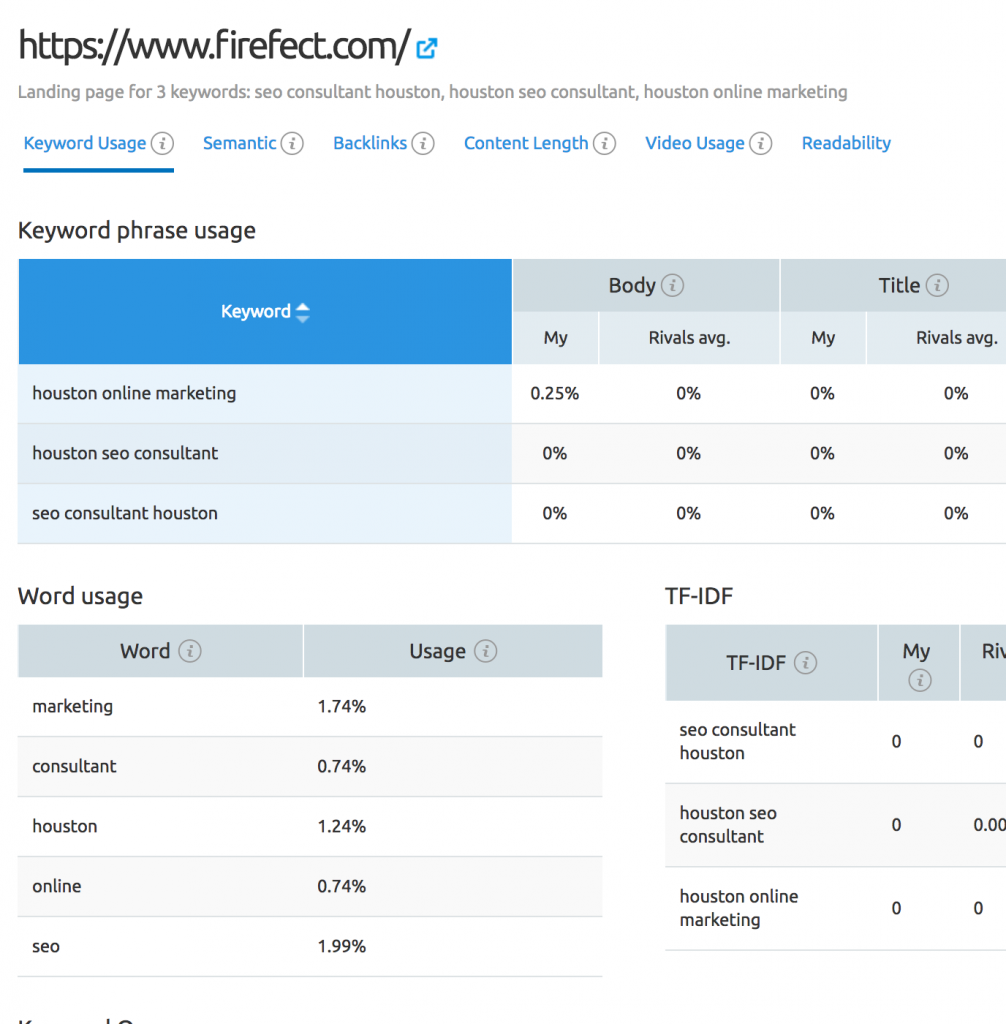
Keyword Phrase Usage
If you look at the Keyword Phrase Usage section, you’ll notice that it compares the keyword phrase density on your web page to your top competitors.
Word Usage
The word usage section simply provides you with the density of each singular word on the page. This tells you which words are more prominent within your content.
Putting the Data into Action
Try balancing your keyword phrase densities so that they are similar to your top ranking competitors. They do not have to be exact. Just keep the densities close.
Once you’ve done that, introduce an optimization that you cannot find in the SEMrush suggestions. This will be the variable you use for testing and optimization. Some examples could be, increasing your keyword density to be above average, implementing more semantic words not within the recommendations, or even using Search Console data for optimization ideas.
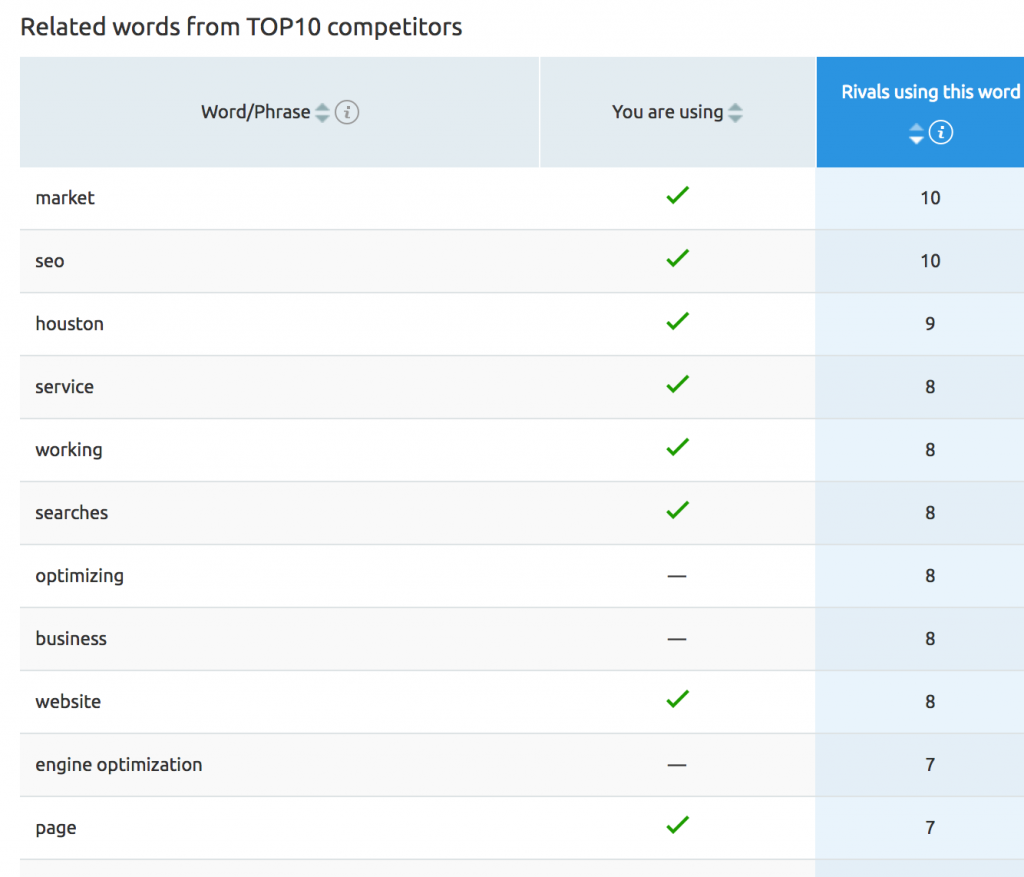
Semantic
Once you’ve finished with the content optimizations, move to the Semantic data. SEMrush presents this data within a table comparing prominent word densities found on your web page to your top 10 competing webpages. The goal here is to words that your top competitors are using within their content that you are not. After identifying those terms, sprinkle them throughout your web page naturally.
Content Length
You will want to make sure that your page’s word count is in line with your top competitors.
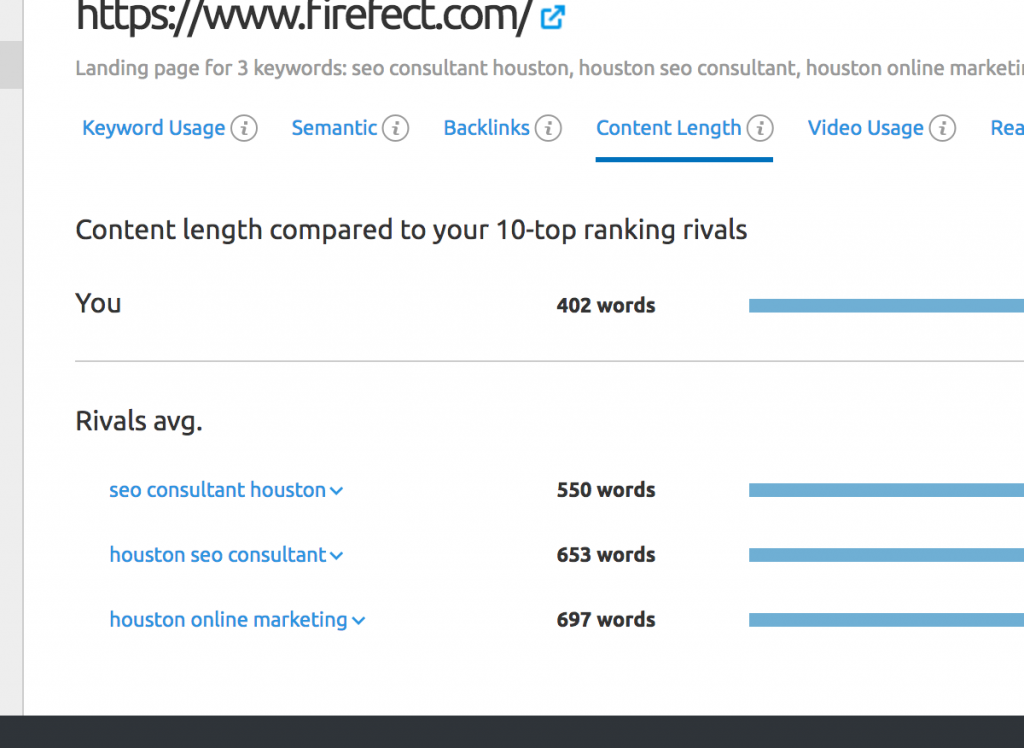
The last two areas you can check out are the Video Usage and Readibility sections. These are recommendations that you shouldn’t ignore, but are self-explanatory for this particular tutorial. These two subjects can go much deeper, but for the sake of the tutorial, we’ll keep it brief.
Other Data Points to Consider
Because the focus of this tutorial is on On-Page optimization, I didn’t discuss backlinks. However, analyzing the backlink data would be the next step in my SEO process. Backlinks are a different beast because they send relevancy signals, popularity signals, authority signals, trust signals, and plenty of other ranking signals. Backlinks are part of Google’s core ranking algorithm and are also the #1 ranking factor to consider.
